Introduction
In today’s software development world, delivering high-quality applications is critical. CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment/Delivery which is a set of practices that automate the process of building, testing, and deploying applications. Let’s break down how CI/CD works and look at real-world examples that make the concept easier to understand.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment/Delivery
CI/CD is a popular DevOps methodology that is designed to automate the steps between writing code and delivering it to users. It ensures faster development, fewer bugs, and smoother releases.
Continuous Integration (CI):
Developers can frequently merge their code changes into a shared repository like GitHub or GitLab. Every change automatically triggers a build and runs tests to detect integration issues early.
Continuous Delivery (CD):
After CI, the code is automatically prepared for deployment by packaging, testing, and validating but may require manual approval before release.
Continuous Deployment (CD):
Every successful build is automatically deployed to production with no manual intervention.
Why CI/CD Matters
CI/CD ensures faster delivery, better collaboration, early bug detection, improved reliability and continuous feedback.
- Faster delivery: Automates testing and deployment, reducing time to market.
- Better collaboration: Developers, testers, and ops teams work seamlessly.
- Early bug detection: Issues are caught during integration instead of after release.
- Improved reliability: Automated pipelines ensure consistency across environments.
- Continuous feedback: Each change triggers feedback to developers instantly.
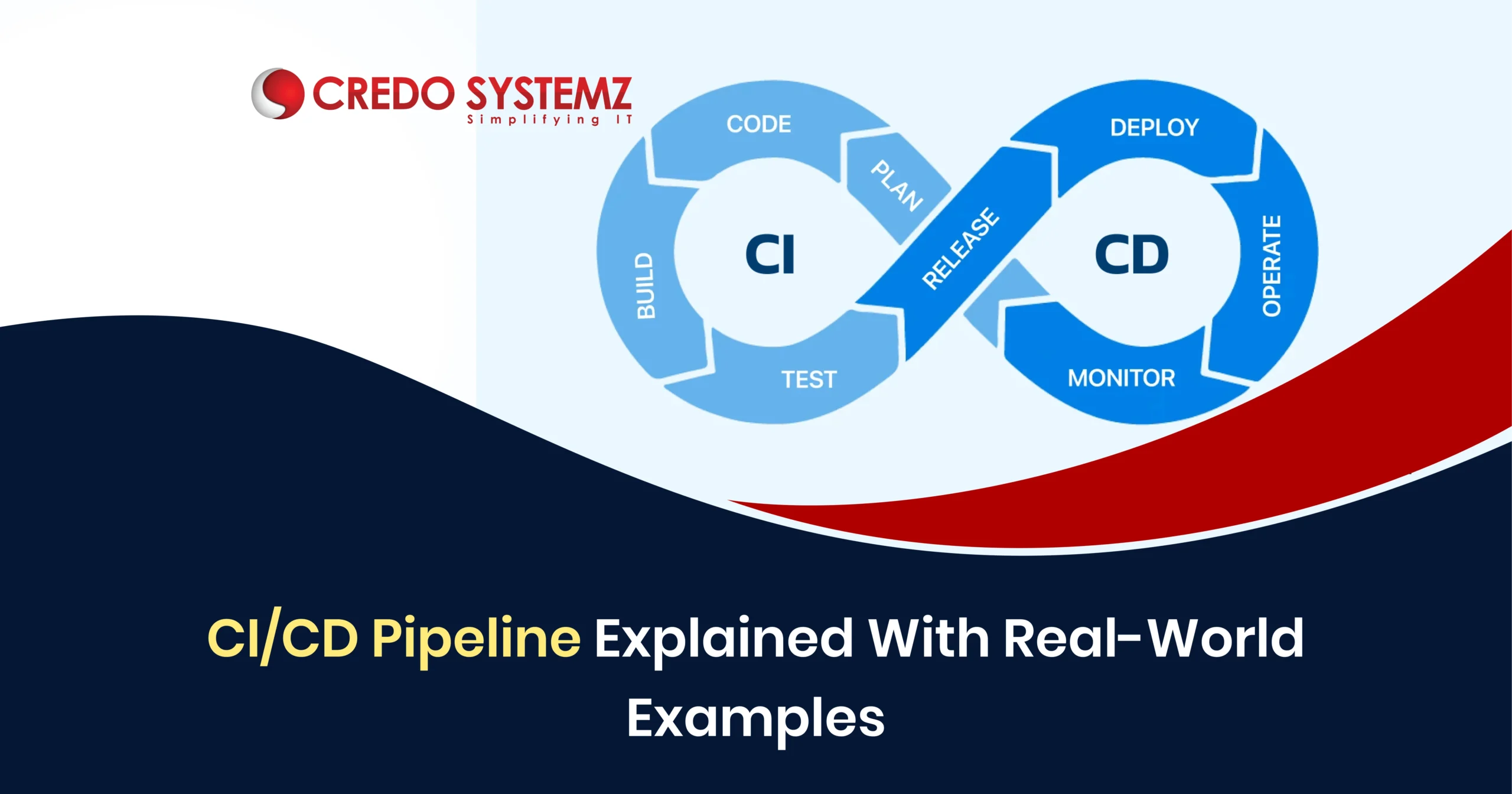
CI/CD Pipeline Stages
A CI/CD pipeline has five main stages:
- Source stage,
- Build stage,
- Test stage,
- Deploy stage,
- Monitor stage
Source Stage:
The process begins when developers commit code to a version control system like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket.
Build Stage:
The source code is compiled, dependencies are installed, and artifacts (like .jar, .war, or .zip files) are generated.
Test Stage:
Automated unit, integration, and functional tests are run to verify code quality.
Deploy Stage:
The tested build is deployed to staging or production environments.
Monitor Stage:
Monitoring tools track performance, logs, and errors to ensure everything runs smoothly after deployment.
Real-World Examples of CI/CD
Example: E-commerce Web Application
Scenario:
An online shopping platform built with Spring Boot (backend) and React (frontend).
Pipeline Flow:
- Developer pushes code to GitHub.
- Jenkins pipeline triggers automatically.
- Maven builds the Spring Boot project.
- JUnit runs automated unit tests.
- Docker container is built and pushed to Docker Hub.
- Kubernetes deploys the container to a staging environment.
- After approval, the app is deployed to production.
Tools Used: GitHub, Jenkins, Maven, JUnit, Docker, Kubernetes.
Benefit: Faster feature delivery and instant rollback in case of issues.
2. Example: Mobile App (Android/iOS)
Scenario:
A team developing a cross-platform app using Flutter.
Pipeline Flow:
- Code is pushed to GitLab.
- GitLab CI/CD builds APK/IPA files automatically.
- Automated UI tests run on emulators.
- Artifacts are uploaded to Firebase App Distribution for QA testing.
- Once approved, release is published to Google Play and App Store.
Tools Used: GitLab CI, Flutter, Firebase, Fastlane.
Benefit: Reduced manual testing time and faster app release cycles.
3. Example: Data Engineering Project
Scenario:
A company using Azure Data Factory (ADF) for ETL workflows and Snowflake for data storage.
Pipeline Flow:
- Data pipeline code is version-controlled in Azure DevOps.
- CI pipeline validates JSON and ARM templates for ADF.
- CD pipeline deploys validated pipelines to test and production environments automatically.
- Monitoring through Azure Monitor ensures workflow reliability.
Tools Used: Azure DevOps, ADF, Snowflake, Power BI, Azure Monitor.
Benefit: Consistent data deployment and reduced manual intervention for data engineers.
Popular CI/CD Tools
| Category | Tools |
|---|---|
| CI/CD Platforms | Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD, GitHub Actions, CircleCI |
| Containerization | Docker, Podman |
| Orchestration | Kubernetes, OpenShift |
| Cloud CI/CD | AWS CodePipeline, Azure DevOps, Google Cloud Build |
| Monitoring | Prometheus, Grafana, Dynatrace |
Best Practices for CI/CD Pipelines
- Keep builds fast — avoid unnecessary steps.
- Automate everything like testing, builds, deployments.
- Use feature flags for safer releases.
- Implement rollback strategies for failed deployments.
- Integrate code reviews and automated code scanning.
- Monitor metrics and alerts continuously.
Final Thoughts
To conclude, CI/CD pipeline is the backbone of modern software development. It helps teams move from manual, error-prone releases to automated, efficient workflows. Whether it’s deploying a web app, mobile app, or data pipeline, CI/CD ensures speed, quality, and reliability. Join Credo Systemz software courses to master CI/CD which is essential for tech jobs.

Join Credo Systemz Software Courses in Chennai at Credo Systemz OMR, Credo Systemz Velachery to kick-start or uplift your career path.
FAQ
The goal of CI/CD is to automate software integration, testing, and deployment processes for faster, more reliable releases.
